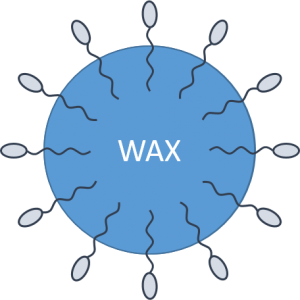
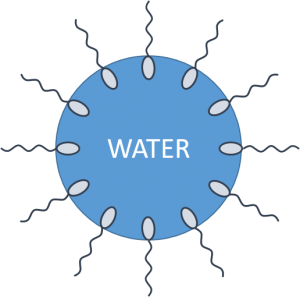
Stabilization of particles (oil or wax) in an aqueous emulsion takes place through the following steps:
- Surfactant ‘wets out’ the wax particles in the aqueous phase
- Surfactant is effectively absorbed at solid/liquid interface
- Surfactant layer reduces energy required to separate particles
- This enables separation under the effect of mechanical shear
- Shear can be provided by milling or dispersing equipment.
- Once the particles are dispersed, the adsorbed surfactant prevents their re-agglomeration.
- Particle stability can be effected by:
- a) electrostatic potential
- b) steric effect, or
- c) a combination of a) & b)